In eCommerce, providing a sense of security to your customers is essential in creating trust and long-term relationships. Part of that mission requires us to stay up to date with possible security concerns that may impact our customers and the safety of their data. A current vulnerability that we should be aware of is OpenSSL’s recent CVE-2022-3602 & CVE- 2022-3786 vulnerabilities.

What is OpenSSL
OpenSSL is an open sources software that we can use to secure our websites. Websites that are secured tend to have “https” in their URL and a small padlock next to their web address, but what those two visual queues mean is that your site has a valid certificate.
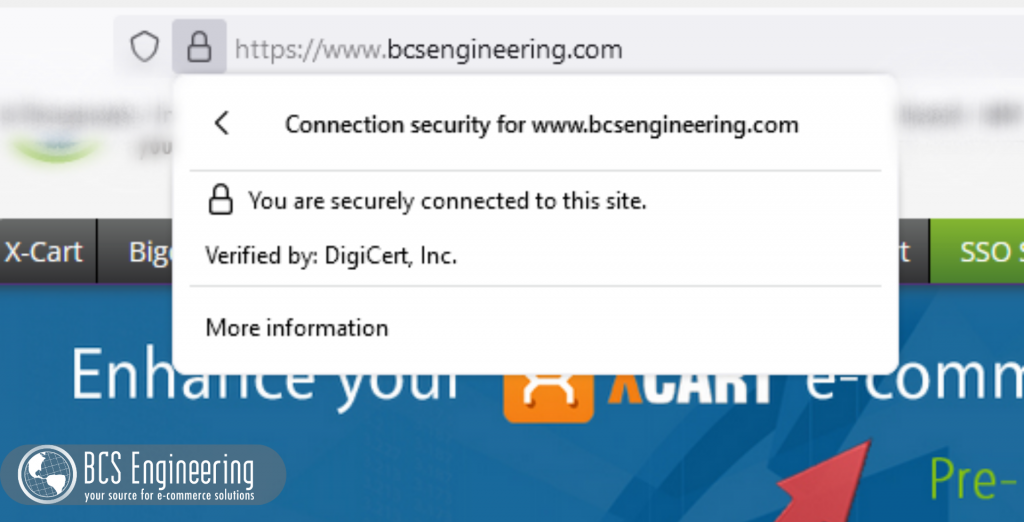
A certificate is a way of establishing that 1) you are who you say you are, and 2) the communications that happen on your site are encrypted. While the contents and creation process of certificates involve multiple steps, they are essentially a bundle of information about your site that is signed by a trusted authority, allowing your customers to also trust your business. OpenSSL is a way to create and implement these certificates on your site.
Why should I care about Certificates?
While sites can run without certificates, web browsers and search engines are very particular about security. Not having a certificate or having an invalid certificate can lead to your site being marked as a risk. Sites deemed questionable will require customers to manually click a button to accept this risk to visit your site. This may result in potential customers leaving your site before even seeing your content.
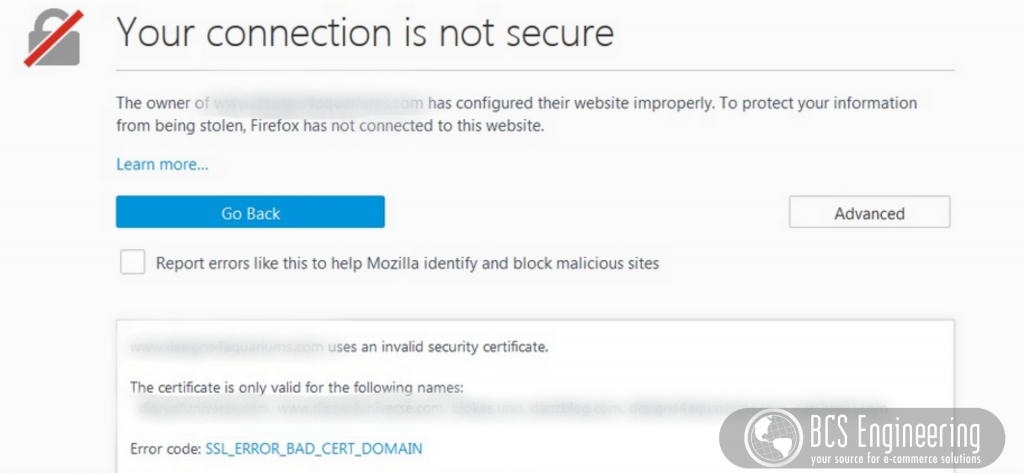
Another downfall to not having certificates is that search engines like Google will rank your site low on their search engines, if not leave your site off of relevant searches entirely. As discussed previously in our blog on Google’s search essentials, having proper security is a bare minimum for Google to consider indexing your site. Organic traffic relies on the searchability on your business, so ensuring that your site has a proper certificate is essential to your online shop’s success.
Beyond that, having safe lines of communication with your customers, especially considering the exchange of financial information in online shops, is imperative to protect your customers and your business. Not having proper security leaves your site open to hackers and attacks, and that can affect the functionality of your site, the privacy of information, and the overall reputation of your business.
What is CVE-2022-3602 & CVE- 2022-3786?
CVE-2022-3602 & CVE- 2022-3786 are vulnerabilities that appeared on October 25th, 2022, that were originally marked at a critical threat vulnerability to those using OpenSSL. OpenSSL’s ranking of risk follows a four-level scale, with critical being the highest. This means that these vulnerabilities affect both common usages of OpenSSL and have a high risk of being exploitable, meaning that someone with malicious intent could use these vulnerabilities to their advantage.
In this case, these vulnerabilities involve a common software weakness called buffer overflow. Buffer overflow is essentially how the internet handles large pieces of information. Just like how we can only carry so many groceries from our cars into our houses after going shopping, the internet can only take so much information at a time. When we try to carry too many bags at once, we may drop something or struggle to successfully carry everything into the house. This vulnerability targets that weakness.
CVE-2022-3602 & CVE- 2022-3786 target the process of proving the validity of a certificate, that a site is who it claims it to be and that it is safe to visit. These vulnerabilities can be acted on after an application or user has manually approved an invalid certificate or has encountered a falsely signed certificate. In turn, a malicious actor could send a bunch of information on this open channel when looking at the certificate and cause one of two things:
- Crash the service to where the user can’t access your site.
- Possibly tell the browser or site to do something, like execute code.
Now, on November 1st, 2022, OpenSSL lowered the risk level of these threats to high, meaning that these vulnerabilities were less exploitable than originally anticipated, but still something to be aware of. This is because both of these vulnerabilities require many factors to be in place to work effectively. Your server must have adopted the specific version of OpenSSL, version 3.06, and our users would have had to accept a bad certificate OR a malicious actor would have had to convince a certificate authority to sign a bad certificate. All these factors are unlikely. With OpenSSL version 3.06 being new, adoption is low. Most users and applications are aware of the risks of accepting bad certificates, and it is not easy to forge a fake certificate that is properly signed.
Who does this effect?
These CVE vulnerabilities can affect those who:
- Interact with OpenSSL.
- Trust third party or untrusted certificates manually or automatically.
What should I do?
If you think you fall into one of those categories as a business owner, the good news is that OpenSSL released a patch that removes the threat of these vulnerabilities. All you have to do is make sure that, if you are using OpenSSL, you update to the newest version, version 3.07. In terms of maintaining future security, make sure your site has a valid certificate and that your site isn’t accepting invalid certificates.